KRT V2 YAML specs
YAML Definition of a KRT file.
The main purpose of KRT V2 is to bring branched workflows on board. This means nodes are now capable of subscribing to several other nodes at the same time, thus workflows are now capable of branching out.
It is advised to previously read and fully understand KRT before moving on to V2, as this page focuses on explaining V2 related changes and new concepts.
Here is an example of an architecture defined by a KRT V2 file, this example is taken from our KRT V2 demo repo:
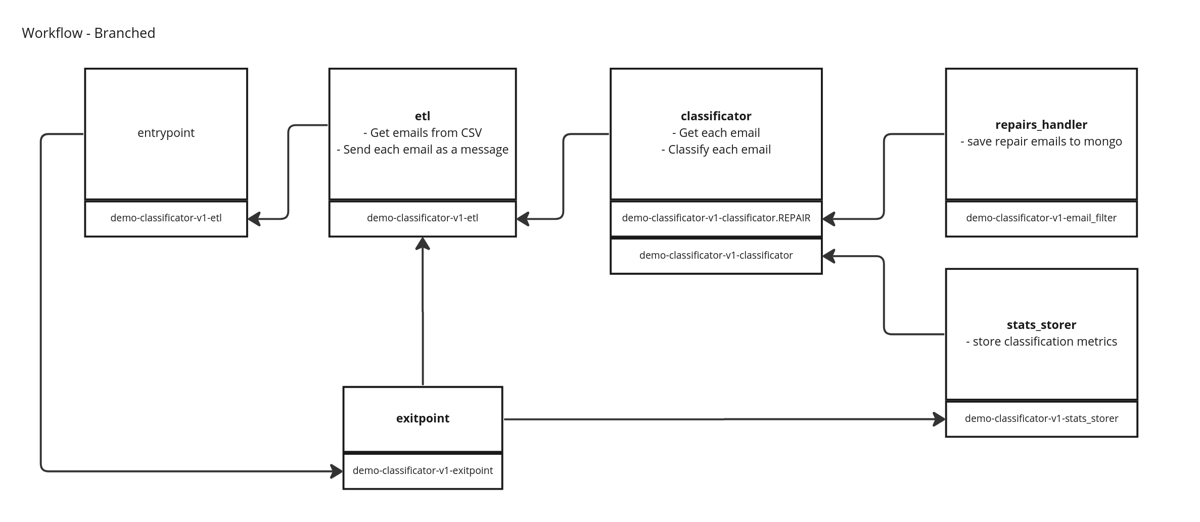
Nodes will publish their results onto their own subject, is up to other nodes whether to subscribe and process its messages or not. This allows for organic growth as nodes can be developed then hooked up to other nodes freely.
Nodes now don’t necessarily have to return a response, they can publish several to none messages to their topics. Thus, instead of returning the message to be published, messages will be published using the function SendOutput provided by the context.
Nodes can choose which subtopic from their own subject they publish to. At the same time, they can choose to take messages from any subtopic of another node. This allows users to filter out messages and reduce stress on nodes.
Nodes can subscribe to one or more subtopics from another node and to various nodes at the same time. To help with filtering, users can set up which handlers are to be executed depending on the request’s origin. Take into consideration nodes can only discern the node from which the request proceeds, not the subtopic or topic. For setup guidance consult Runner SDK.
The exitpoint is a user defined node and can take up any name, however it has to be later assigned in the krt.yaml file to the exitpoint attribute. Users can only define one exitpoint as this is the final node to which the entrypoint will subscribe.
An exitpoint is required in all workflows. As the exitpoint is the only node that will communicate back to the entrypoint, it is recommended to handle merge strategies in it.
Also, if users wish to implement “early exit” and “early reply” strategies, they should subscribe the exitpoint to nodes emitting these types of messages.
The KRT YAML file serves the same purpose as its predecessor. However, now nodes are declared and defined inside the workflows, an exitpoint must be described per workflow and a v2 tag must be added to the krtVersion field.
Users must define subscriptions in the node’s definition. The names s in the subscriptions list must match the declared node’s names. ‘entrypoint’ is the reserved name for the entrypoint KRE provides. In order for a node to subscribe to the entrypoint just type the reserved name in its subscriptions.
Learn about the fields in the KRT YAML specs.
YAML Definition of a KRT file.